
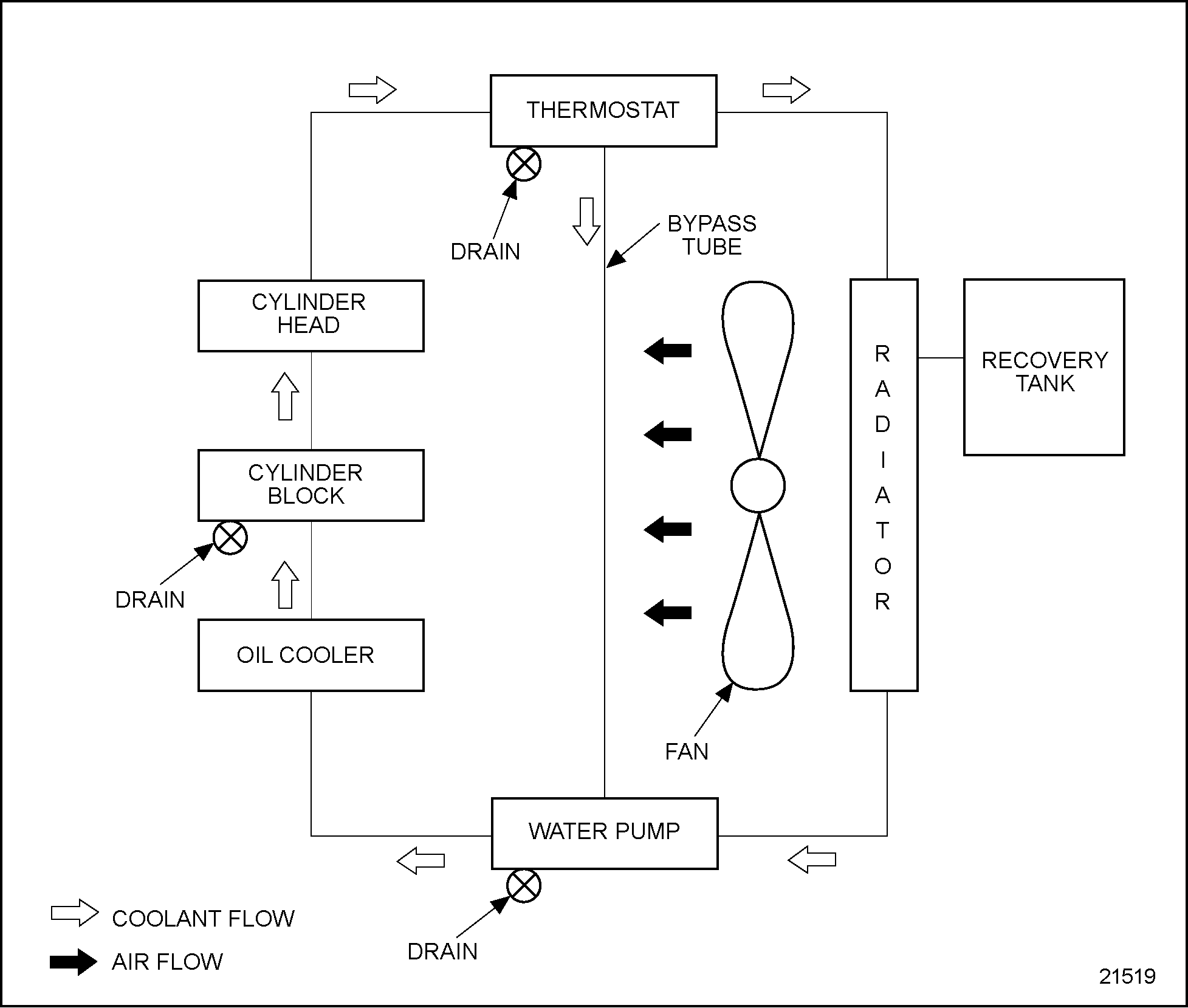
The engine produces heat and coolant flows through it to cool it down. These tubes and fins are usually pressed together into an aluminum or plastic shell, which contains all the components within it. Radiators consist of a collection of metal tubes filled with fins in which liquid coolant flows in order to dissipate heat that is produced by the engine. Radiators are an essential part of a car’s cooling system, helping to ensure optimal engine performance and efficiency. The impeller has blades that spin the coolant around and creates a lower-pressure area that pulls in more coolant from the radiator. Coolant actually comes from the bottom of the radiator and into the center of the impeller. The water pump sits on the engine block with the impeller inside. Being driven by the crankshaft belt means that as soon as the engine is started, the water pump starts running.Ī water pump consists of a housing made from cast aluminum with a couple of mounting points for the timing system, a shaft that runs through the body, an impeller, and a pulley attached to a flange. This is where the water pump gets its power from. It is the same belt that drives the alternator. The water pump is located on the front of the engine and has a pulley that is driven by a belt from the crankshaft. The car water pumps are so powerful that they circulate all of the coolant around the engine about twenty times in one minute. If the engine is sitting in one place, it will start to boil next to the hottest parts of the engine (engine cylinders). The coolant then travels around the cylinders, then goes up to the head where it cools the valves, and finally comes back out of the cylinder head towards the radiator to get cooled down.īasically, the purpose of the water pump in a car is to keep the coolant circulating.

When the engine is first started, the water pump pulls cold coolant from the bottom of the radiator and sends it to the front of the engine block. Below, I will present to you the main parts of a car cooling system and how they work. This is where the cooling system comes into place. However, without a proper cooling system in place, the ideal engine temperature can easily be surpassed. The ideal operating temperature for an engine is about 200 degrees Fahrenheit or about 90 degrees Celsius. The engine runs hot due to the constant combustion occurring in the engine cylinders. If the temperature of the coolant is way too high on the radiator side, the coolant temperature sensor will trigger the cooling fan. When the main valve on the thermostat opens, the cold coolant from the radiator starts flowing to the engine side, and in return, the hot coolant from the engine side flows to the radiator. Once the coolant reaches a temperature between 160 to 190 degrees Fahrenheit, the bypass valve of the thermostat will close and the main valve will open. Eventually, the temperature of the coolant will increase by absorbing the heat from the engine. This way, the engine can get up to a working temperature faster. The coolant actually bypasses the radiator and recirculates through the engine. While the coolant is cold, the bypass valve on the thermostat stays open and the coolant is recirculated to the engine. When you first start your engine, both the engine and the coolant are cold. The thermostat is always soaked in coolant and that is how it actually measures the temperature. The thermostat is actually a valve that regulates the flow of the coolant. As the coolant absorbs the heat from the engine cylinders, it heads toward the radiator where with the help of a thermostat, it gets redirected toward an overflow tank where it gets cooled. The coolant flows from the lower radiator tank to the engine block, then to the cylinder head, and towards the outlet of the radiator. When the engine is started, the water pump begins to pump the cold coolant from the lower radiator tank into the coolant passages around the engine cylinder. The heater core receives hot coolant and releases this heat into the cabin.A coolant temperature sensor measures the temperature of the coolant that flows around the engine and determines the current temperature of the engine.A thermostat determines when the coolant is too hot and opens up a passage to an expansion tank where the coolant cools down.The radiator stores the coolant when the vehicle is turned off.The water pump is in charge of circulating coolant around the engine.
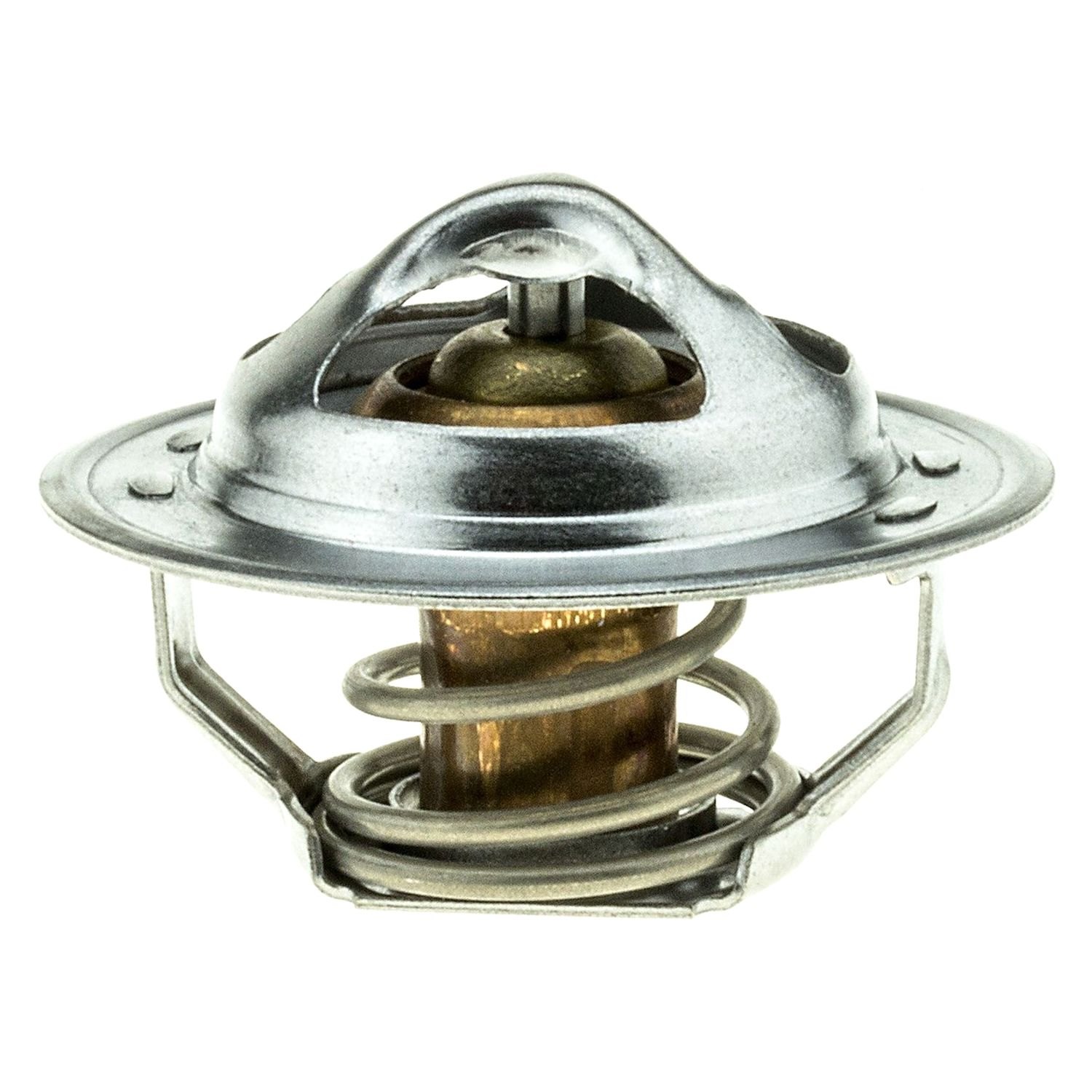

When it gets hot, the coolant then goes to the expansion tank to cool down before going on another cycle.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
